We present a silicon nanowire-based field-effect transistor biosensor with Schottky barriers for highly specific and sensitive human α-thrombin detection. The active sensor area is decorated with thrombin-binding aptamers as receptor molecules. Each sensor chip is integrated into a microfluidic device for flow-through measurements. Instantaneous detection is provided by real-time monitoring of FET transfer curves. With this approach, thrombin concentrations between 200 pM and 200 nM are detected in a label-free, real-time manner, covering a wide dynamic range and enabling to distinguish between healthy and pathological levels. The development of simple, miniaturized devices for blood protein detection is highly interesting for medical diagnostics.
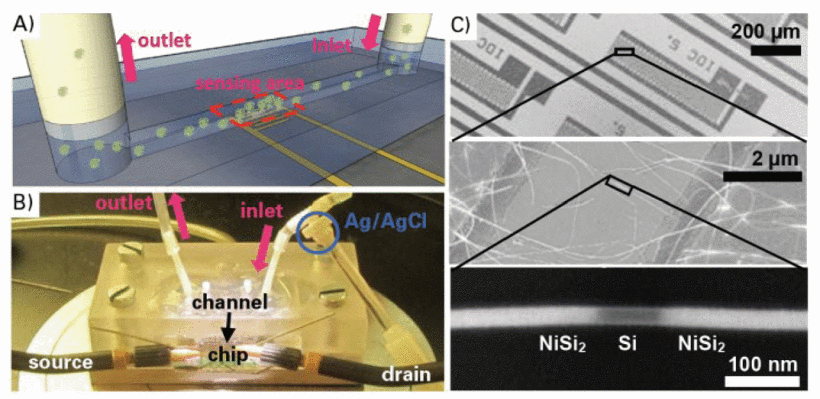
We present a silicon nanowire-based field-effect transistor biosensor with Schottky barriers for highly specific and sensitive human α-thrombin detection. The active sensor area is decorated with thrombin-binding aptamers as receptor molecules. Each sensor chip is integrated into a microfluidic device for flow-through measurements. Instantaneous detection is provided by real-time monitoring of FET transfer curves. With this approach, thrombin concentrations between 200 pM and 200 nM are detected in a label-free, real-time manner, covering a wide dynamic range and enabling to distinguish between healthy and pathological levels. The development of simple, miniaturized devices for blood protein detection is highly interesting for medical diagnostics.
