Nanoparticle-enhanced coatings of bone implants are a promising method to facilitate sustainable wound healing, leading to an increase in patient well-being. This article describes the in vitro characterization of osteoblast cells interacting with polyelectrolyte multilayers, which contain detonation nanodiamonds (NDs), as a novel class of carbon-based coating material, which presents a unique combination of photoluminescence and drug-binding properties. The cationic polyelectrolyte, namely polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA), has been used to immobilize NDs on silica glass. The height of ND-PDDA multilayers varies from a minimum of 10 nm for one bilayer to a maximum of 90 nm for five bilayers of NDs and PDDA. Human fetal osteoblasts (hFOBs) cultured on ND-PDDA multilayers show a large number of focal adhesions, which were studied via quantitative fluorescence imaging analysis. The influence of the surface roughness on the filopodia formation was assessed via scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The nano-rough surface of five bilayers constrained the filopodia formation. The hFOBs grown on NDs tend to show not only a similar cell morphology compared to cells cultured on extracellular matrix protein-coated silica glass substrates, but also increased cell viability by about 40%. The high biocompatibility of the ND-PDDA multilayers, indicated via high cell proliferation and sound cell adhesion, shows their potential for biomedical applications such as drug-eluting coatings and biomaterials in general.
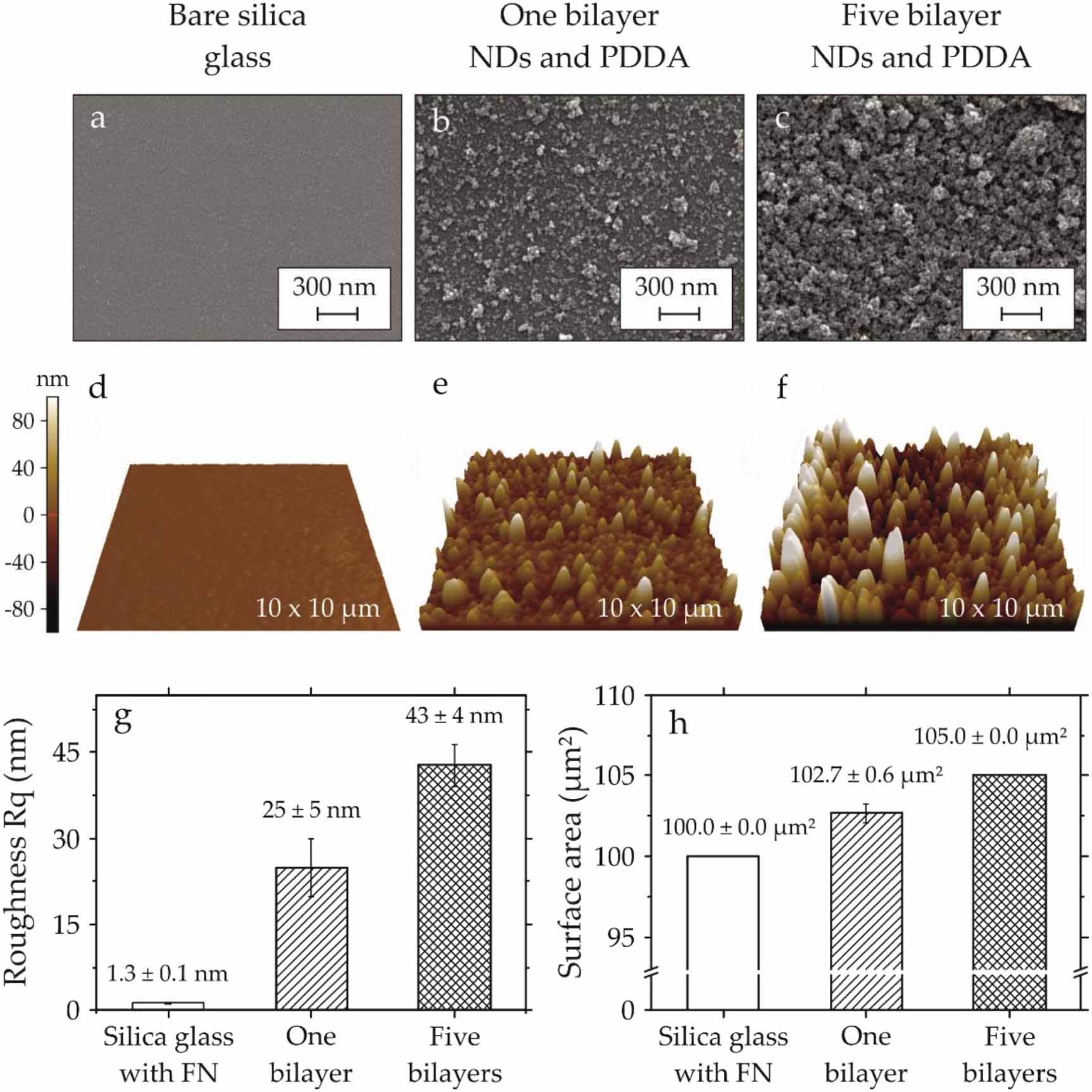
Nanoparticle-enhanced coatings of bone implants are a promising method to facilitate sustainable wound healing, leading to an increase in patient well-being. This article describes the in vitro characterization of osteoblast cells interacting with polyelectrolyte multilayers, which contain detonation nanodiamonds (NDs), as a novel class of carbon-based coating material, which presents a unique combination of photoluminescence and drug-binding properties. The cationic polyelectrolyte, namely polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA), has been used to immobilize NDs on silica glass. The height of ND-PDDA multilayers varies from a minimum of 10 nm for one bilayer to a maximum of 90 nm for five bilayers of NDs and PDDA. Human fetal osteoblasts (hFOBs) cultured on ND-PDDA multilayers show a large number of focal adhesions, which were studied via quantitative fluorescence imaging analysis. The influence of the surface roughness on the filopodia formation was assessed via scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The nano-rough surface of five bilayers constrained the filopodia formation. The hFOBs grown on NDs tend to show not only a similar cell morphology compared to cells cultured on extracellular matrix protein-coated silica glass substrates, but also increased cell viability by about 40%. The high biocompatibility of the ND-PDDA multilayers, indicated via high cell proliferation and sound cell adhesion, shows their potential for biomedical applications such as drug-eluting coatings and biomaterials in general.
