Vinylene‐linked two‐dimensional polymers (V‐2DPs) and their layer‐stacked covalent organic frameworks (V‐2D COFs) featuring high in‐plane π‐conjugation and robust frameworks have emerged as promising candidates for energy‐related applications. However, current synthetic approaches are restricted to producing V‐2D COF powders that lack processability, impeding their integration into devices, particularly within membrane technologies reliant upon thin films. Herein, we report the novel on‐water surface synthesis of vinylene‐linked cationic 2DPs films (V‐C2DP‐1 and V‐C2DP‐2) via Knoevenagel polycondensation, which serve as the anion‐selective electrode coating for highly‐reversible and durable zinc‐based dual‐ion batteries (ZDIBs). Model reactions and theoretical modeling revealed the enhanced reactivity and reversibility of Knoevenagel reaction on the water surface. On this basis, we demonstrated the on‐water surface 2D polycondensation towards V‐C2DPs films that show large lateral size, tunable thickness, and high chemical stability. Representatively, V‐C2DP‐1 presents as a fully‐crystalline and face‐on oriented film with in‐plane lattice parameters of a=b=~43.3 Å. Profiting from its well‐defined cationic sites, oriented 1D channels, and stable frameworks, V‐C2DP‐1 film possesses superior bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anion (TFSI‐)‐transport selectivity (transference, t−=0.85) for graphite cathode in high‐voltage ZDIBs, thus triggering additional TFSI‐‐intercalation stage and promoting its specific capacity (from ~83 to 124 mAh g‐1) and cycling life (>1000 cycles, 95% capacity retention).
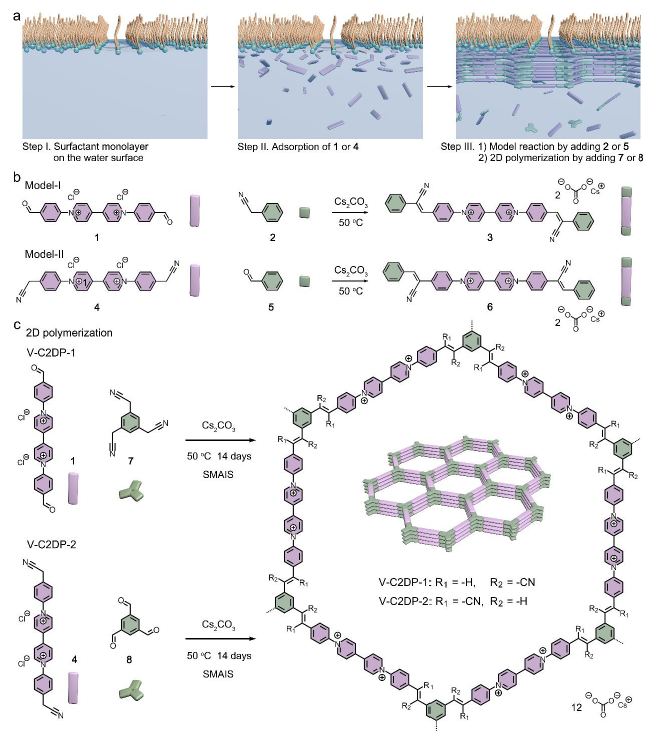
Vinylene‐linked two‐dimensional polymers (V‐2DPs) and their layer‐stacked covalent organic frameworks (V‐2D COFs) featuring high in‐plane π‐conjugation and robust frameworks have emerged as promising candidates for energy‐related applications. However, current synthetic approaches are restricted to producing V‐2D COF powders that lack processability, impeding their integration into devices, particularly within membrane technologies reliant upon thin films. Herein, we report the novel on‐water surface synthesis of vinylene‐linked cationic 2DPs films (V‐C2DP‐1 and V‐C2DP‐2) via Knoevenagel polycondensation, which serve as the anion‐selective electrode coating for highly‐reversible and durable zinc‐based dual‐ion batteries (ZDIBs). Model reactions and theoretical modeling revealed the enhanced reactivity and reversibility of Knoevenagel reaction on the water surface. On this basis, we demonstrated the on‐water surface 2D polycondensation towards V‐C2DPs films that show large lateral size, tunable thickness, and high chemical stability. Representatively, V‐C2DP‐1 presents as a fully‐crystalline and face‐on oriented film with in‐plane lattice parameters of a=b=~43.3 Å. Profiting from its well‐defined cationic sites, oriented 1D channels, and stable frameworks, V‐C2DP‐1 film possesses superior bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anion (TFSI‐)‐transport selectivity (transference, t−=0.85) for graphite cathode in high‐voltage ZDIBs, thus triggering additional TFSI‐‐intercalation stage and promoting its specific capacity (from ~83 to 124 mAh g‐1) and cycling life (>1000 cycles, 95% capacity retention).
